Ever tried to connect two pipes and found the perfect fitting just doesn’t exist? Picture this: you’re working on a custom project, and you need a specialized connection – a customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter. You search online, but nothing quite fits your specifications. This can be frustrating, especially when precision is key. This post will explore how you can craft your own, personalized solutions. You’ll gain valuable insights into the process of creating a customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter, from design to print, equipping you with the knowledge to bring your ideas to life and save you time. Prepare to simplify your projects and elevate your creation process.
Key Takeaways
- Learn the fundamental concepts behind a customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter.
- Discover the essential steps for designing your adapter using CAD software.
- Understand the 3D printing techniques suitable for creating reliable pipe connections.
- Explore various materials and their properties to choose the right one for your adapter.
- Gain insight into the post-processing methods to optimize the adapter’s performance.
- Realize the numerous applications where a custom Y pipe adapter can be used.
The Basics of a Customizable 3D Printing Y Pipe Adapter
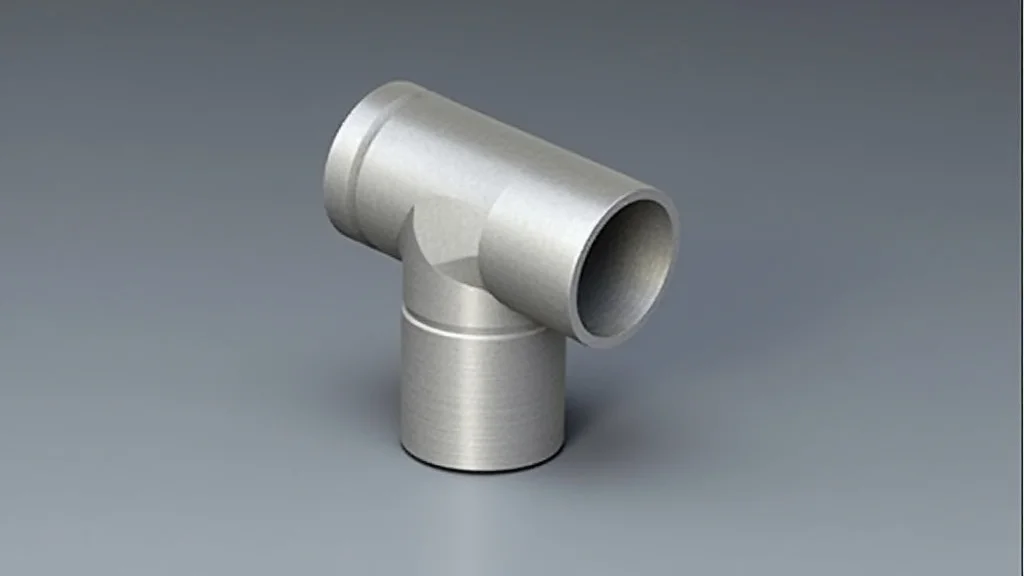
A Y pipe adapter, at its core, is a fitting used to split or merge the flow within a pipe system. It’s shaped like the letter “Y,” with a single inlet and two outlets (or vice versa). The traditional versions, usually made from metal or plastic, can come in standard sizes and angles. But what happens when you need a unique size, an unusual angle, or a material not readily available? That’s where a customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter shines. It provides the freedom to design and manufacture a fitting specifically for your needs, eliminating limitations imposed by off-the-shelf components. This means no more compromises, and you get exactly what your project needs.
What is 3D Printing and How Does It Work?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, builds three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital design. Think of it like a sophisticated version of building with LEGO bricks, but instead of plastic blocks, you use materials like plastic, metal, or even ceramic. The process starts with a 3D model created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This model is sliced into thin layers, and the printer follows these instructions to deposit material, one layer at a time, until the object is complete. The exact method changes depending on the 3D printing technology used. For example, some printers use a laser to melt plastic powder, while others deposit liquid resin that hardens when exposed to light.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most common type of 3D printing, especially for hobbyists. It involves melting plastic filament and extruding it through a nozzle, layer by layer, to build the object. Think of it like a hot glue gun, but with precise control.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid plastic. It offers high precision and is great for detailed parts, such as complex adapters that require specific tolerances.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon. It can create complex shapes and strong parts without needing support structures, which simplifies the printing process for complex designs like a Y pipe adapter with unusual angles.
FDM is a great option for experimenting with customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter designs because of its accessibility and affordability. It’s often used for prototypes and functional parts where extreme strength isn’t the primary requirement. However, the resolution can sometimes be less detailed compared to other methods.
SLA is perfect if you need a smooth surface finish and intricate details in your adapter. The finished parts are usually stronger and more aesthetically pleasing. However, the resin materials can be more expensive than FDM filaments.
SLS provides a great balance of strength, detail, and material choices. Adapters made with SLS can often withstand higher temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for industrial applications. It is less common for hobbyists due to the cost.
Key Components of a Customizable 3D Printing Y Pipe Adapter
A customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter isn’t just a simple connection; it involves careful consideration of several key elements. The design must accommodate the specific size and type of pipes you’re connecting, the angles required for the branching, and the overall structural integrity needed for the application. The adapter’s success hinges on these essential parts. These factors impact its performance, ensuring the efficient flow of fluids or gases. Moreover, they dictate its durability and suitability for the intended purpose, whether it’s for household plumbing, automotive systems, or industrial applications.
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: These are the openings that connect to the pipes. They must match the size, shape, and connection type (e.g., threaded, barbed, or slip-fit) of the pipes you’re using. Careful measurement and design are essential to ensure a tight, leak-proof seal.
- Y-Branch Angle: The angle at which the two outlets split from the inlet. This is critical for flow dynamics and pressure loss. Different angles have different impacts on the fluid or gas flow.
- Wall Thickness: The thickness of the adapter’s walls is key to its structural integrity. It affects the adapter’s ability to withstand pressure and external forces. If the walls are too thin, the adapter may fail under pressure.
- Internal Surface Finish: The smoothness of the interior surfaces affects the fluid or gas flow. A rough surface creates friction, increasing pressure loss and potentially leading to buildup or corrosion.
The design of the ports must accommodate the method of connection. If using threads, ensure the thread type (NPT, BSPT, etc.) and size are correct. For slip-fit connections, accurate sizing is crucial to avoid leaks. Remember to include features for sealing, such as o-ring grooves or sealing surfaces.
A wider angle typically reduces pressure loss, but it might require a larger adapter. A narrower angle might save space, but it could lead to increased turbulence. The optimal angle depends on the specific requirements of your system, considering factors like flow rate and the fluid’s properties.
The correct wall thickness is determined by the material used, the operating pressure, and any external stresses. A thicker wall usually means greater strength, but it can also increase material usage and print time. Use the minimum thickness that provides the required strength and durability. If you are using plastics, thicker walls may also reduce the warping of the part.
A smooth internal finish is important, and you can achieve it through the design and post-processing. Some 3D printing processes, like SLA, produce smoother surfaces. You may need to use techniques like sanding or applying a sealant if the print has a rough finish.
Designing Your Customizable 3D Printing Y Pipe Adapter
The design process begins in the digital space. The goal is to create a 3D model that can be “printed” by a 3D printer. This involves using CAD software, which stands for Computer-Aided Design. This software allows you to visualize, design, and modify your adapter to match your precise requirements. It’s a bit like sketching, but on a computer, and the result is a digital blueprint of your customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter.
Choosing the Right CAD Software
The market has a range of CAD software, from free, user-friendly options to professional-grade programs. Each offers a varying level of features, complexity, and capabilities. The key is to select software that aligns with your skill level and project needs. Some programs are easy to pick up, while others require extensive training. Start with something simple if you are new to CAD, such as Tinkercad or Fusion 360, and move to more complex software as needed.
- Beginner-Friendly Options:
Tinkercad is a browser-based, easy-to-learn program, perfect for beginners. Its drag-and-drop interface lets you create basic shapes and combine them into more complex designs. OnShape is another great option, especially if you need cloud-based storage and collaboration features. Its free version is sufficient for basic designs.
- Intermediate CAD Software:
Fusion 360 is a powerful program with a wide range of features. It combines CAD, CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) capabilities. It has a free version for personal use, which offers a great combination of features and affordability. FreeCAD is a robust open-source alternative to Fusion 360, with more advanced capabilities.
- Professional CAD Software:
SolidWorks and AutoCAD are leading industry standard CAD software. They offer comprehensive tools and are usually used in professional engineering settings. While they offer advanced features, they can be costly and have a steeper learning curve.
The Modeling Process: Steps and Techniques
Once you’ve selected your software, it’s time to build your model. This is where you bring your idea to life. It will involve careful measurement, precise design, and a good understanding of how to use the software’s tools. Be patient, as creating the perfect customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter design may require several iterations. Accuracy and attention to detail are key to a successful print.
- Measurements: Gather the essential data: the diameter of your pipes, the connection type (threaded, barbed, slip-fit), and the desired branch angle. Accuracy at this stage is crucial.
- Sketching: Begin by sketching the basic shapes. Create the profile of the inlet and outlets, as well as the Y-branch. This involves using the software’s 2D sketching tools to define the key features.
- Extruding and Joining: Extrude the sketches to create the 3D form. Combine the parts to build the adapter. At this stage, you’ll bring the 2D sketches into the 3D space. Extrusion involves giving the sketches depth.
- Adding Details: Include important features such as threads, sealing surfaces, and any structural supports. This can involve using tools to cut threads, add chamfers, and create grooves.
- File Export: Export the model in STL format, which is the standard format for 3D printing. This converts your design into a format the 3D printer can understand.
Measure your pipes carefully using calipers. Threaded connections require precise measurements for the thread type (NPT, BSPT, etc.) and size. For slip-fit connections, measure the outside diameter. Knowing these measurements will ensure your adapter connects correctly. If possible, consider measuring an existing fitting for reference.
Sketching involves creating the 2D shapes that will form the basis of your 3D model. Most software uses a “sketch-extrude” approach, where you draw a shape and then extrude it into a 3D form. Use the line, circle, and arc tools to create the profile of each port and the connecting branch.
Extrude each part of the design, such as the inlet, the two outlets, and the connecting section. Make sure to define the correct wall thickness and length. Next, use the software’s tools to combine these parts. This involves aligning and merging the various components to create a single, unified object.
This is where you refine your design. Add the details needed for functionality. Create threads on the inlet and outlets using thread-generating tools if your pipes are threaded. Also, include o-ring grooves or other sealing surfaces to prevent leaks. Chamfers and fillets on the edges of the design can also add durability.
Once you are happy with the model, export it as an STL file. This file contains all the necessary data to build your adapter. Make sure to review your model before exporting to avoid potential issues during printing. Check for any errors or inconsistencies that could affect the final result.
Design Considerations: Angles, Flow, and Connections
The overall performance of your adapter heavily relies on a well-thought-out design. The angles of the Y-branch and the connection methods you choose will impact flow characteristics and ease of installation. A customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter allows you to optimize these factors, but it’s essential to understand the implications of each design choice. Careful design decisions can result in improved flow, reduce pressure drop, and ensure a reliable connection.
- Branch Angles: The angle between the inlet and outlets affects the flow characteristics. Wider angles tend to reduce pressure drop. But, they might increase the overall size of the adapter. Narrower angles can conserve space, but they might lead to increased turbulence.
- Threaded vs. Slip-Fit Connections: Different connection types have their own benefits and drawbacks. Threaded connections are easy to install, while slip-fit connections can provide a more compact design. The connection type can influence the material choice and the strength required.
- Internal Flow Paths: Ensure the internal passages are smooth and unobstructed to minimize pressure drop and turbulence. Avoid sharp edges or abrupt changes in direction.
Choose an angle that balances your flow needs. Research the best angle for your application. If you’re designing for a specific fluid, you can consult fluid dynamics resources or run simulations to test different angles. Some designs might use curves instead of sharp angles to reduce turbulence.
Consider the environment and ease of installation. Threaded connections are great if you anticipate needing to disassemble the system. Slip-fit connections can be simpler to set up, but they require accurate sizing. You’ll need to account for thread standards (NPT, BSPT, etc.) or the outer diameter for slip-fit connections.
Carefully consider the internal geometry of your adapter. The smoother the interior, the better the flow. You can use CAD tools to create smooth transitions between the inlet and outlets. Make sure there are no areas where fluid or gas could get trapped or cause build-up.
Choosing the Right Materials for Your 3D Printed Adapter
Selecting the right material is vital for a functional and durable customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter. The perfect material depends on factors such as the fluids or gases involved, the operating temperature and pressure, and any chemical resistance requirements. Many materials are available for 3D printing, each with unique properties that influence your adapter’s performance and lifespan. Considering these factors ensures you create an adapter that meets the specific demands of the intended application.
Material Options: Plastics, Metals, and Composites
The range of materials available for 3D printing has grown rapidly, offering plenty of options for your adapter. Plastics are a versatile choice, offering a great balance of cost, ease of use, and properties. Metals and composites provide increased strength and temperature resistance. Choosing the right material requires an understanding of what each option brings to the table and what it does not.
- Plastics: PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable plastic, suitable for low-stress applications. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is impact-resistant, making it a better option for more demanding tasks. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) provides excellent durability and chemical resistance. Nylon (Polyamide) is known for its strength and flexibility.
Choose your plastic based on the requirements of your project. PLA is good for prototypes, but it might soften in high temperatures. ABS and PETG provide enhanced durability. Nylon provides both strength and flexibility, making it a good choice for pressure applications.
- Metals: Stainless steel provides high strength and corrosion resistance. Aluminum offers a good strength-to-weight ratio. Titanium is exceptionally strong and lightweight, ideal for applications where weight is a factor.
Metal 3D printing is a great choice when high strength and resistance to extreme conditions is required. Stainless steel is versatile for general use, while aluminum is a lighter alternative. Titanium is used where both strength and lightweight properties are needed, although metal printing is more expensive.
- Composites: Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers offer exceptional strength and stiffness. Glass fiber-reinforced polymers provide enhanced impact resistance. These materials can improve the overall strength and performance of the adapter.
Composites can be tailored to the exact requirements of your adapter. They provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios and are suitable for high-stress applications. Consider the properties of the matrix and reinforcement material. The choice will influence the temperature resistance, impact resistance, and durability of your adapter.
Material Properties: Strength, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
The properties of the chosen material are just as crucial as the material type. These properties determine the adapter’s ability to withstand the forces and conditions of its operating environment. Some materials are strong, while others can resist the effects of heat or chemicals. Understanding these properties ensures that the customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter is suitable and safe for its intended purpose. Careful attention to these details will prevent premature failure and ensure optimal performance.
- Strength: The material’s ability to withstand stress and deformation. Tensile strength indicates how much force the material can bear before breaking. Yield strength indicates the point at which the material starts to deform permanently.
- Temperature Resistance: The material’s ability to withstand high or low temperatures without losing its properties. The melting point determines the highest temperature the material can handle. The glass transition temperature is the point where a material transitions from a rigid to a more flexible state.
- Chemical Resistance: The material’s ability to resist the effects of chemicals, such as corrosion or degradation. The resistance level varies for each chemical. The operating fluid can determine the material’s longevity.
Choose materials with appropriate strength, considering the pressure and forces your adapter will face. Higher strength might be needed for applications involving high pressures or physical stress. Make sure your design is strong enough and that the material can handle the load.
If your adapter will be exposed to high temperatures, choose a material with a high melting point and glass transition temperature. Some plastics are good for low temperatures, while others remain stable in high-temperature environments. Choose a material that exceeds the expected operating temperatures.
Ensure the material is compatible with the fluids flowing through your adapter. Research the material’s resistance to the specific chemicals. Some plastics are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, while others are susceptible to certain substances. If you are unsure, consider performing compatibility tests or seeking advice from material experts.
Printing and Post-Processing Your Adapter
Once you’ve designed your adapter and chosen the perfect material, it’s time to print it. This is where your digital design becomes a physical object. The printing process brings the digital model to life, layer by layer, based on the specific 3D printing technology you’ve selected. Post-processing steps are often needed to refine the adapter’s properties. These steps can include removing support structures, smoothing surfaces, and enhancing mechanical properties. The final product should meet your exact design and performance needs.
3D Printing Techniques Suited for Adapter Production
The best 3D printing technique will depend on the materials used, the level of detail needed, and the overall budget. The most common techniques used are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each of these techniques has advantages and disadvantages, and knowing these factors will help you make the right choice for your customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM is a cost-effective choice for general-purpose adapters. It is ideal for prototypes and parts that don’t need high precision. It is best for simple designs and is accessible for beginners due to the low cost and ease of use.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA is well-suited for adapters needing high resolution and smooth surfaces. This is a great choice when details, such as precise threads or intricate geometries, are important. The technique uses liquid resin and a laser to create precise parts.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS is suitable for durable adapters made from nylon or other strong materials. SLS is usually employed when the adapter requires a robust design, high strength, and resistance to environmental factors. SLS produces parts that need no support structures, which can be beneficial for complex geometries.
FDM is a suitable option if you’re working with plastics. However, you might want to consider the layer lines and lower resolution when selecting this option. The technology might not be suitable for intricate details or applications where the surface finish is a concern.
SLA is a good choice if you need a smooth surface finish. The technology produces parts with a high level of detail. However, the use of liquid resin may present limitations on material selection.
SLS provides a solid balance of material options and durability. The technique is ideal for functional parts. However, the equipment and materials are usually more expensive than other processes.
Post-Processing Steps: Finishing and Enhancements
After the adapter is printed, you’ll likely need to perform some post-processing steps. These processes refine the adapter, enhance its performance, and prepare it for use. The necessary steps vary based on the printing technology, the material used, and the intended application. These steps may involve removing support structures, smoothing surfaces, and adding finishes. Careful post-processing ensures the customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter meets your precise specifications and performance needs.
- Removing Support Structures: Many 3D printing processes require support structures, especially for overhanging features. These support structures need to be carefully removed after printing.
- Surface Finishing: Surface finishing improves the adapter’s appearance and performance. Smoothing the surface reduces friction, improves fluid flow, and can enhance the visual appeal.
Sanding is a great technique to smooth out layer lines. Apply fillers or sealants for a smoother, more leak-proof finish. Smoothing the surface improves the adapter’s overall aesthetic.
- Leak Testing and Sealing: Check the adapter for leaks after printing. You may want to conduct tests or seal the adapter to ensure a reliable connection.
Connect your adapter to the system and run tests for leaks. If leaks occur, you can use sealants, such as epoxy, to fix them. Ensure all sealing surfaces meet your needs.
FDM often needs support structures, while SLS does not. Remove supports carefully to avoid damaging the adapter. Some support materials dissolve in water or chemicals, making removal easier. Proper removal ensures the adapter’s final geometry is accurate.
Applications of a Customizable Y Pipe Adapter
A customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter is versatile and adaptable to various applications. The ability to design and create a fitting tailored to your exact needs allows for innovative solutions across various sectors. From simple household repairs to complex industrial applications, these adapters are vital for creating a dependable system. This adaptability extends to many fields, from DIY projects to professional applications.
Household and DIY Projects
DIY enthusiasts and homeowners can use custom Y pipe adapters for a variety of tasks. These adapters can solve unique plumbing challenges or adapt to specific configurations. The adapters offer a cost-effective solution for various projects and are easily adapted to changing needs. This flexibility makes them an invaluable asset for home improvement tasks. Here are several examples of use cases.
- Plumbing Modifications: Repairing or modifying household plumbing systems to accommodate unique connections.
Create a custom adapter to connect pipes of different sizes or types. Design a solution to install a new fixture. The freedom to create an adapter specifically for the need ensures a leak-free and efficient plumbing system.
- Irrigation Systems: Creating personalized irrigation systems for your garden.
Design a system to adapt different hose sizes or connect to sprinkler systems. These adapters ensure an efficient water supply to the garden. Custom designs eliminate the need to compromise with off-the-shelf components.
- Appliance Connections: Adapting appliance connections.
Create adapters to connect dishwashers, washing machines, and other appliances. Ensure a proper fit between the appliance and the existing water or drainage lines. They provide a safe and effective connection.
Automotive and Engineering
In the automotive and engineering sectors, custom Y pipe adapters offer specialized solutions. They provide precise fittings for unique applications. The ability to design and produce custom adapters contributes to system efficiency. These are essential for prototypes, performance upgrades, and specialized machinery. This functionality can enhance systems performance and facilitate innovation.
- Performance Upgrades: Customizing intake or exhaust systems.
Design adapters to optimize the airflow in engines. Improve the efficiency and performance of vehicles. Adapt the adapter to your specifications, allowing for greater performance improvement.
- Prototype Development: Creating custom fittings for early-stage prototypes.
Design and print adapters to connect various components during product development. The speed and flexibility of 3D printing allow for quick iterations. Adapters make the prototyping process quicker and more efficient.
- Fluid Systems: Adapting fuel, coolant, or oil lines in various industrial applications.
Create a perfect fit and ensure optimal fluid flow. Make sure the adapter is compatible with the fluids it will carry. Ensure the adapter can withstand the environment.
Industrial and Specialized Applications
In industrial and specialized industries, custom Y pipe adapters find vital applications. These adapters provide solutions for complex systems. Their reliability and customizability are essential for many applications. They can tackle difficult configurations with ease, leading to greater efficiency and optimization. These applications ensure reliability and provide solutions for specialized equipment.
- Chemical Processing: Handling specific chemicals and fluids.
Design adapters using chemically-resistant materials to withstand harsh substances. Ensure compatibility and safety during chemical processes. Provide a safe and efficient distribution of chemicals.
- Medical Devices: Creating custom connectors for medical equipment.
Create adapters compatible with medical-grade materials, and meet the strict requirements of medical applications. Ensure reliability and safety in medical devices. Create specialized solutions for unique equipment needs.
- Aerospace: Designing and manufacturing components for aircraft.
Produce lightweight and high-strength adapters for aircraft applications. The customizability allows for precise design and functionality. Ensure all parts meet the stringent demands of aerospace engineering.
Common Myths Debunked
Myth 1: 3D-Printed Adapters Are Not Durable
In the past, this was more true, but modern 3D printing, combined with proper material selection and post-processing, allows you to create highly durable adapters. Strong materials like nylon, metal, and composites, printed with appropriate settings, can withstand significant pressure, temperature, and wear. The durability of a customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter depends on the material, design, and print parameters.
Myth 2: 3D Printing Is Only For Prototyping
While 3D printing is fantastic for prototypes, it’s also suitable for end-use parts. The cost-effectiveness and quick turnaround of 3D printing makes it the best choice for producing custom adapters. With the correct materials and post-processing, you can produce functional and durable adapters.
Myth 3: Designing Your Own Adapter Is Too Complex
With readily available CAD software and tutorials, designing a customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter has become easier than ever. Even if you’re not an expert, user-friendly CAD programs and online resources will assist you in creating basic adapter designs. The overall complexity depends on the desired level of intricacy.
Myth 4: 3D-Printed Adapters Are Always Expensive
The cost of a 3D-printed adapter depends on several things, including the material, printer, and finishing steps. For simple designs and materials, the costs are usually low, particularly when compared with custom manufacturing. The cost-efficiency is also influenced by the scale of your operation. Costs may be higher for complex designs.
Myth 5: 3D Printing Isn’t Accurate Enough for Pipe Fittings
Modern 3D printing offers a great level of precision. SLA and SLS technologies can create accurate adapters with tight tolerances. The key to accurate prints is to understand your printer, choose appropriate settings, and perform post-processing (such as sanding) to improve the dimensions. Accurate designs will meet your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What’s the best CAD software for a beginner?
Answer: Tinkercad is an excellent choice for beginners because it’s user-friendly and browser-based.
Question: What material is best for high-pressure applications?
Answer: Nylon or metal (like stainless steel) is the best choice for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. You may also want to use carbon fiber.
Question: Can I print an adapter without supports?
Answer: Some 3D printing methods, like SLS, don’t require support structures. However, techniques such as FDM usually do.
Question: How do I ensure my adapter is leak-proof?
Answer: Design in sealing surfaces (like o-ring grooves), use appropriate threads, and conduct leak tests after printing. Apply sealants if necessary.
Question: How long does it take to print a Y pipe adapter?
Answer: The printing time varies based on the design’s complexity, the printer, and the chosen material. It could range from a couple of hours to a full day.
Final Thoughts
The customizable 3d printing y pipe adapter is a tool for innovation and creativity. It enables you to solve unique connection challenges and create custom solutions. From DIY home improvement to specialized engineering applications, the versatility of 3D printing unlocks possibilities. By mastering the fundamentals, you can create high-performance components. Explore the different materials, technologies, and methods to create your custom fittings. Consider the advantages of 3D printing and how they can improve your projects. Start designing and printing your custom adapters. The freedom to create personalized solutions can revolutionize your approach to projects. Your projects have become much simpler and more adaptable.